Understanding the C if-else Statement: A Complete Guide
In C programming, the if-else statement is a decision-making statement. This statement decides whether the statements or block of code should be executed or not based on conditions.It is one of the simplest and most important conditional statements in C language.
Using the if-else statement, the flow of execution of a program can be changed or modified.Basically, the if-else statement controls the flow of a program and is also termed a control flow statement.It decides whether a certain statement or block of statements will be executed or not based on a given condition.
For example, if a given condition is true, then the statements or block of statements inside the if body are executed; otherwise, the code in the else block will be executed.
if-else allows code to be executed conditionally based on a boolean condition. if-else statements make the block of code more readable.
For a better understanding of how the if-else statement works, learn the following example.
Let’s take an expression pqr:
If the "pqr" expression is true:
• The statements inside the body of the if control statement are executed.
• Statements inside the body of the else statement are ignored.
If the "pqr" expression is false:
• The statements inside the body of the if are ignored.
• Statements inside the else part are executed.
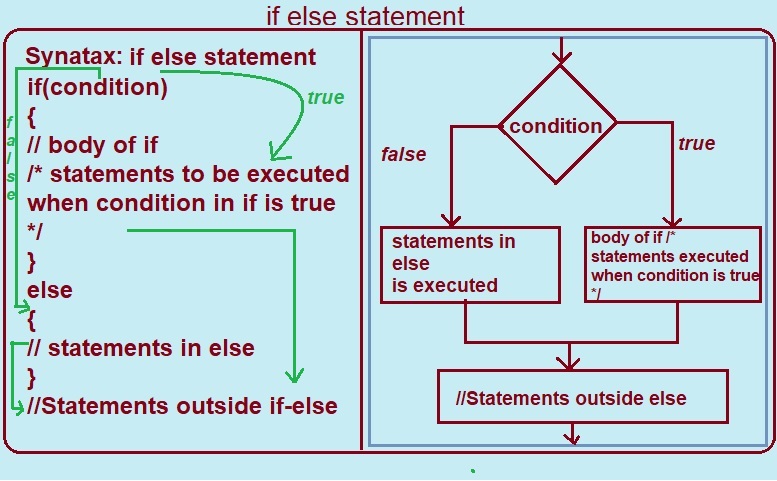
Syntax: if-else statement
if (condition)
{
// if body
// Statements to execute if condition is true
}
else
{
// Statements to execute if condition is false
}
1. The program control first reaches the if statement and tests the condition.
2. If the test condition is true:
• The if block is executed. The // if body and // statements to execute if condition is true are executed. In practice, some executable code should be written here.
3. If the test condition evaluates to false:
• The else block (// Statements to execute if condition is false) is executed.
4. Afterward, the program control continues to the remaining statements below inside the program.
5. The condition in the syntax evaluates to true (i.e., 1) or false (i.e., 0).
The C language instructions or statements can be a single line or multiple lines of code enclosed within curly braces { }.
Given diagram illustrates the syntax and flowchart of the if-else statement.
Let's learn how the syntax (if-else statement) works from the given diagram.
We know that program execution starts from the top and proceeds to the end.
After the step-by-step successful execution of the program, the control falls into the if block.
Then, the flow jumps to the Condition and begins testing it.
1. If the tested condition is true or its result is true, then the statements inside the if block are executed, i.e., // body of if
/* Statements to be
executed when
conditions in if are true */
After the successful execution of the above code, control exits the if block and proceeds to execute the statements outside the if-else.
2. If the tested condition is false, then the code or statements inside the else block are executed, i.e., "statements in else".
Note that "statements outside if" always execute regardless of whether the condition is true or false.
Example 1: C program to illustrate the use of if-else statement
/* C program to check if a given number is even or odd using if-else statement */
#include
int main()
{
int x;
printf("\n Enter any number");
scanf("%d",&x);
if(x%2==0) /* test-condition */
{
printf("\n %d is an even number",x);
}
else /* else executes when condition is false */
{
printf("\n %d is an odd number",x);
}
return 0;
}
Output:
Enter any number
7
7 is an odd number
Program Explanation:
The above program illustrates the use of an if-else statement to check whether the given number is odd or even.
1. In the program, we declare an integer variable int x; to store the numeric value.
2. Then, we use printf("\n Enter any number"); to display the message "Enter any number" on the console, and scanf("%d",&x); to take input from the user, which in this case is 7 and store it in the variable x.
3. Next, we use an if statement with the test expression x%2==` to check whether the number is even or odd. Since 7%2 gives a remainder of 1, the expression x%2==0 evaluates to false.
4. Because the condition is false, the else block executes, and the statement printf("\n %d is an odd number",x); runs, producing the output: "7 is an odd number".
Note that %d is a format specifier used as a placeholder for the integer value of x, so the output displays "7 is an odd number".