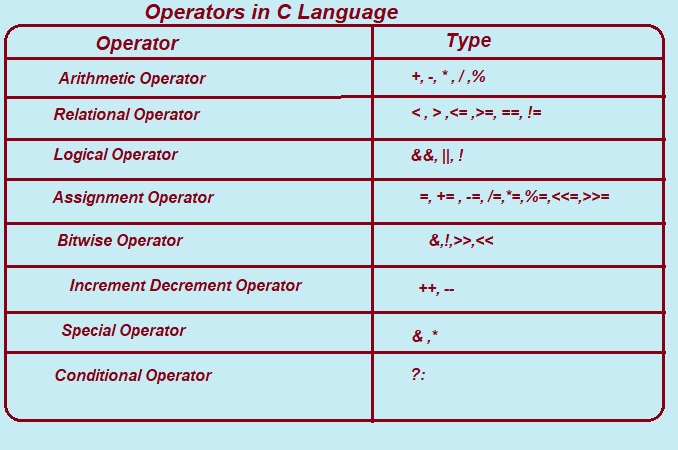
1. Arithmetic Operators:
Arithmetic operators are the symbols that perform addition, subtraction, multiplication, division, exponentiation, and modulus operations. Examples.
+ addition operator
- subtraction operator
* multiplication operator
/ division operator
% Modulo.
2. Relational Operators:
| Symbol | Operation | Example | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
| < | Less Than | a < b | True if a is Less than b |
| > | Greater than | a > b | True if a is Greater than b |
| == | Equal | a==b | True if a is equal b |
| != | Not equal | a!=b | True if a is not equal b |
| <= | Less than or equal | Greater than or equal | True if a is greater than or equal to b |
| >= | Greater than or equal | a>=b | True if a is greater than or equal to b |
3. Logical Operators:
| Symbol | Operation | Example | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
| && | Logical AND | (x>5) &&(y<5) | It returns true when both conditions are True |
| || | logical OR | (x>=10)||(y>=10) | It returns when any one of the condition is True |
| ! | logical NOT | !(x>=5) | It returns True when value of x is not greater or equal to 5 |
4. Assignment Operators:
| Symbol | Operation Performed |
|---|---|
| = | Assignment |
| %= | Remainder Assignment |
| += | Addition Assignment |
| -= | Subtraction Assignment |
| <<= | Left-shift Assignment |
5. Bitwise Operators:
>> : Right Shift Operator e.g a>>b
<< : Left Shift Operator e.g a<< b
6. Increment Decrement Operators
++ Increment the value of variable by 1 e.g a=5;
a++; // increment the value of a by 1 i.e a=a+1
-- Decrement the value of variable by 1 e.g a=5;
a--; //decement the value of a by 1 i.e a=a-1
7. Special Operators:
& :This operator is used to get the address of the variable.
* :
This operator is used as a pointer to a variable.
e.g.*a where * is a pointer to the variable a.
8. Conditional Operator(?:):
The conditional operator is also called a ternary operator because it requires three operands. This operator is used for decision making. In this operator, first we verify a condition, then we perform one operation out of the two operations based on the condition result. If the condition is TRUE the first option is performed, if the condition is FALSE the second option is performed. The conditional operator is used with the following syntax.
Condition ? TRUE Part : FALSE Part;
in fig. Detail operator Structure.