Pointer to structure: a pointer to a structure is a variable that stores the memory address of a structure. It allows us to manipulate and indirectly access the members of the structure using pointer arithmetic.
Pointer variable holds the address of the structure.
Pointer to structure in C programming is used to create complex data structures such as trees, linked lists, graphs, and so on.
Let understand the pointer to structure step by step.
Pointer to Structure in C programming.
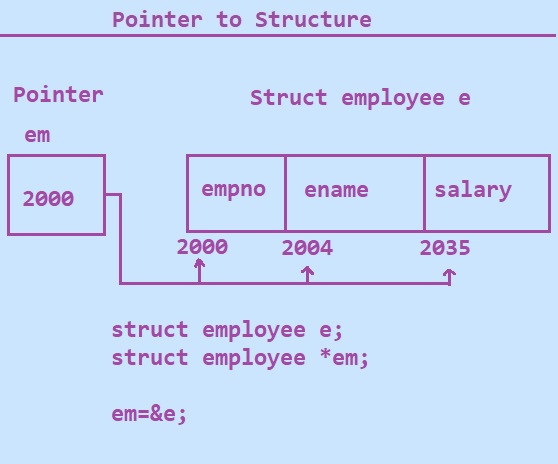
1. Declaration:
Pointer to structure in C programming is defined using the syntax:
struct structName *ptr;
Here, struct is the keyword used to declare structure.
structName represents the name of the structure.
ptr is the name of the structure pointer variable.
For example − struct employee *e;
2. Accessing structure member:
Is the process of retrieving or modifying the value of a specific members within a structure in C programming language.
The structure member can be accessed in two ways the syntax is as follows.
1.Using . (dot) membership operator :
structure_variable.member_name;
Here, 'structure_variable' is the name of the structure variable of the structure type, and `member_name` is the name of a member we want to access.
2. Using -> Operator :
It is explained below how to access the pointers to structures.
This operator (->) is the combination of a minus (-) operator and a greater than (>) relational operator. -> operator is used to access the members of the union or struct that a pointer variable refers to.
Syntax:
(pointer variable)->(variable) = value;
Program to show the usage of pointers to structures and -> operator
#include
struct employee{
int empno;
char ename[30];
float salary;
};
int main ( ){
struct employee e;
struct employee *em;
printf("enter empno, ename, salary:");
scanf ("%d%s%f", &e.empno, e.ename, &e.salary);
em = &e;
printf ("Details of the Employee are");
printf ("Employee Number = %d", em->empno);
printf ("Name = %s", em->ename);
printf ("Salary =%f", em->salary);
return(0);
}
Output:
The program produce the following result −
enter empno, ename, salary:
100 Ajay 45000
Details of the Employee are:
Employee Number = 100
Name = Ajay
Salary =45000.000000
C program that explain the functioning of pointer to structure
#include<stdio.h>
struct product
{
int srno;
float price;
int qty;
};
int main()
{
struct product *pdPtr, p;
pdPtr =&p;
printf(“\n Enter Product Information:\n”);
printf("Enter Srno: \n");
scanf("%d", &p.srno);
printf("Enter product price\n: ");
scanf("%f", &p.price);
printf(“Enter product Quantity:\n”);
scanf(“%d”,&p.qty);
printf("\nProduct Information: ");
printf("\nSrno: %d ", pdPtr->srno);
printf("\n Price: %f", pdPtr->price);
printf(“\n Quantity: %d”,pdPtr->qty);
return 0;
}
Output:
Enter Product Information
Enter Srno: 451
Enter product price: 60.45
Enter product Quantity:80
Product Information:
Srno:451
Price:60.450000
Quantity:80
Previous Topic:-->> Pointers to Function in C. || Next topic:-->>Types of Pointer in C.
Other Topics:
Variables and Identifiers
Relational Operators
if-else statements
Switch case
While Loop
Infinite while Loops
C FOR Loop
Infinite for Loops
Continue in Loops
One Dimensional Array
Two Dimensional Arrays
Read and Display 2D Arrays
Types of functions
Passing Array To Functions
Nesting of Function
Array vs Structure
Array of Structure
Structures and Functions
Structures Within Structures
Use Of Pointers In C
File Handling In C
Loops FAQ
Arrays FAQ
count vowels in a file
Function FAQ
Conditional Statements Assignments
For Loops Assignments
Arrays Assignments
Function Assignments
Structure Assignments
Pointers Assignments
Files Assignments
Storage classes Assignments
Binary Files
count words,lines in a file
Copy files
Update File
Continue in Loops
break in Loops
Difference Between While and Do while
difference while do..while & for
malloc
calloc
Storage Classes
Operators MCQ
Conditional Statements MCQ
Loops MCQ
Arrays MCQ
Function MCQ
Structure MCQ
Pointers MCQ
Files MCQ
Storage classes MCQ