malloc() in C programming.
This tutorials covers the concept of dynamic memory allocation in C programming, which allows allocating memory at runtime according to the program’s needs using functions like malloc(), calloc(), realloc(), and free(). The article focuses on the malloc() function in detail, explaining its syntax, advantages and disadvantages, and providing an example to help understand the concept of dynamic memory allocation.
Table of Contents
a. Introduction.
b. Dynamic Memory Allocation.
c. The malloc in C Programming Language
d. Example of malloc in C .
e. Advantages of malloc() in C .
f. Disadvantages of malloc() in C Programming .
Introduction:
The malloc() is a C library function for dynamic memory allocation. Dynamic memory allocation means allocating memory to variables at runtime depending on the needs of the program.
Arrays variables and scalar variables in C programs are memory bound or have static memory, which means they already have a fixed amount of memory set by the C compiler. An integer takes up 2 bytes or 4 bytes of memory, a floating point number takes up 4 bytes, and so on.
Note: The size occupied may vary for different processors.
When we define an array of any type, the C compiler automatically allocates memory(static memory) equal to its size.
Following are the Problems that arises when static memory is allocated to array:
i. When a program uses few bytes of memory allocated to an array, it wastes the rest of the memory.
ii. When the memory allocated to the array is small and the program needs to allocate more space at run time or dynamically.
When you want to allocate memory to an array dynamically or run time ,the dynamic allocation function helps to allocate memory at run time in C program.
In this tutorial section we will learn about malloc() function and its use in C programming. This article will help you understand the difference between static memory allocation and dynamic allocation.
Dynamic Memory Allocation
Dynamic memory allocation in C is the process in which we allocate or free blocks of memory during program execution. The header file <stdlib.h> contains four functions malloc(), calloc(), realloc() and free(), which are used to dynamically allocate memory in our system. This can also be called the process of heap memory usage, where we can change the size of a variable or a data structure (like an array) while executing the program using library functions.
Dynamic Memory Allocation in c programming Language is considered as a very important concept and is used in almost every Data Structures like Stacks, Dynamic Arrays,Linked Lists, Queue, etc.
Dynamic memory allocation is used in almost every data structure such as linked list, queue, stack, dynamic array, etc. and considered to be a very important field of data structures.
C programming language provides following four library functions for dynamic memory allocation.
malloc()
Malloc() is a C library function used to allocate a block of memory in a section (in bytes) of the memory heap of a specified size when executing a C program.
calloc()
calloc() is a method in C that is also used to allocate blocks of memory in the heap section, but is more commonly used to allocate sequences of blocks of memory (contiguous memory) as arrays of elements. Is done for. It is also located in the <stdlib.h> header file.
realloc()
realloc() is also a method in C that is commonly used to reallocate memory blocks, reallocating here means changing the size of a previously allocated memory block using the malloc() or calloc() methods. increase or decrease. It can also be used to automatically allocate or completely deallocate memory blocks.
free()
free() as the name suggests is used to deallocate or free a memory block previously allocated using calloc() and malloc() functions during run-time of a program.
The malloc() in C Programming Language
In this section we will discuss dynamic memory allocation using malloc in C programming language. Malloc() is a predefined library function for memory allocation. Malloc() is used to allocate a specified size of memory block at the time of program execution. This means it makes dynamic memory allocation at run time when the programmer don’t know how much memory space the program needs.
As per the need we can change the size of allocated memory space at any time during program execution. It uses a pointer to locate the memory address and the default value of this pointer is void. To define the size malloc() uses the sizeof() function. sizeof() is a predefined C library function that returns the size of a variable.
Let Study malloc() function step by step in Detail.
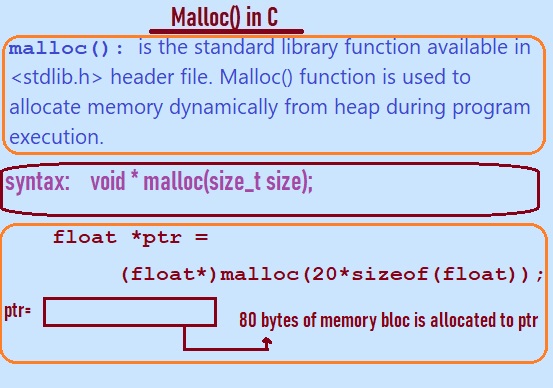
malloc(): is the standard library function available in <stdlib.h> header file.
Malloc() function is used to allocate memory dynamically from heap during program execution.
Here's is a step by step explanation how malloc() works in C program:
1.Function prototype:
Function prototypes is the declaration of a function that declares and define the type of value passed to the program and returned from the function.
The prototype for malloc() function is declared in the <stdlib.h> header file in C Language.
The Syntax :
void *malloc(size_t size);
void *: The malloc() function returns a void pointer means it can implicitly cast to any pointer type in c program.
Size_t size: is the only single argument to this function , size specifies the total number of bytes to allocate.
malloc() returns a pointer to the allocated memory. If malloc() fails to allocate memory it returns NULL.
2.Memory Allocation:
When you call malloc(), it requests a block of memory of the specified size from the heap, which is a region of memory set aside for dynamic memory allocation during program execution.
When the Malloc( ) function is called , the function request area of memory or a block of memory of the size specified. an area of memory or block of memory is allocated dynamically during program execution.
3.Dynamic Memory: dynamic memory allocation in c allows us to allocate memory during program run time or execution instead of compile time. Dynamic allocation is essentially useful when we do not know how much memory needs at compile time.
4. Returns a Pointer: malloc() function returns a void pointer to the allocated memory block. The type of this pointer is of void *, so we can explicitly convert or cast it to any pointer type before using it in the program. For example:
float *ptr = (float *)malloc(20 * sizeof(float));
5. Error Handling: in some situations the malloc() function fails to allocate memory space if there is not sufficient memory available on the heap area. In such scenarios , the returns a null pointer (NULL). It is very important to check the return value to handle such cases gracefully.
Let understand the example:
float *ptr = (int *)malloc(20 * sizeof(float));
if (ptr == NULL)
{
// executes the code here when allocation fails
}
6. Memory Alignment:
The memory specified by this Malloc() function is properly allocated to any type of variable. This means we can use it for any data type found in a C program.
7. Memory Leak:
A common problem of the malloc() function is that it does not free the allocated memory when it is not useful . This concepts leads to memory leaks, where memory is allocated but never released. To free the memory allocated by malloc(), use the standard library free() function.
consider the example:
float *ptr = (float *)malloc(20 * sizeof(float));
free(ptr); // Free the memory
C Program using malloc() function in c, to create a dynamic memory allocation for float array elements.
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stlib.h>
int main()
{
float* fptr;
// allocate memory dynamically using malloc()
fptr = (float*) malloc (6 * sizeof(float));
if(fptr==NULL)
{
printf("OOPS! No space available try another day. \n");
}
else{
printf("Memory has been allocated successfully!. \n");
for(int i=0;i<6;i++)
{
fptr[i] = i*.23
}
//display the array elements
printf("The array Values are: \n");
for(i=0;i<6;i++)
{
printf("\n%.2f",fptr[i]);
}
}
free(fptr);
}
OUTPUT
Memory has been allocated successfully!.
The array Values are:
0.00
0.23
0.46
0.69
0.92
1.15
Advantages of malloc() in C
1. malloc() function allows us to allocate memory at run time .
2. The size of allocated memory can be change at any point in the program using malloc().
3. The pointer points to the first element and works like a array in C.
Disadvantages of malloc() in C Programming
1. Malloc() is not used in embedded system..
2. We need to remember the memory size or space while using the malloc() function for allocating memory dynamically.
Previous Topic:-->> Other directives in C. || Next topic:-->>calloc() in C.