In the C programming language, we learned what is pointer?
Pointers in c programming are variables which stores the address of another variable. When a memory is allocated to a variable, pointer points to the address of the variable. Unary operator or dereference operator (*) is used to declare a variable and it returns the address of the memory allocated allocated.
Pointer to an array in C programming.
Let us understand what is pointer to an array in C programming?
A pointer to an array is variable which is used to store the address of the first value of an array. It points the address of memory block of an array variable. Pointer to an array allows us to manipulate and access the elements of the array using pointer arithmetic.
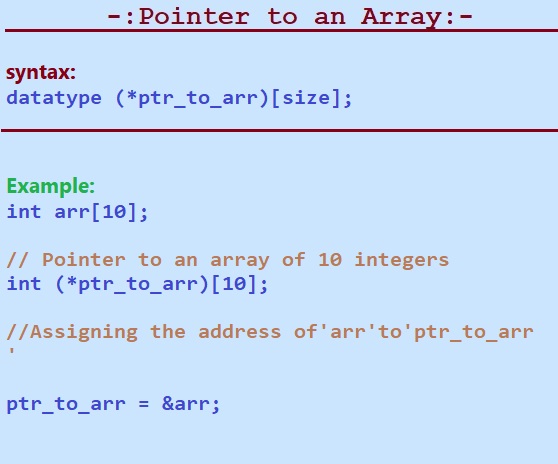
Following is the syntax to declare a pointer to an array in C:
datatype (*ptr_to_arr)[size];
In the given above syntax ‘data type’ is a data type of an elements in the given array.
Data type can be any of a valid data type supported by C language.
` ptr_to_arr is the name used to the pointer variable, and `size` is the size of the array.
If you wish to assign the address of an array to a pointer, just use the array name without the square brackets ([]).
Let understand from the given example:
int arr[10];
int (*ptr_to_arr)[10]; // Pointer to an array of 10 integers
ptr_to_arr = &arr; // Assigning the address of 'arr' to ' ptr_to_arr '
You can then use pointer arithmetic to access the elements of the array through the pointer.
Note : when a pointer to an array is used, we need to dereference the pointer using the `*` operator before accessing .
C program for Pointer to an array of 5 integers in C language.
#include <stdio.h>
int main()
{
int arr[10] = {11, 21, 13, 14, 51,20,40,50,90,70};
int (*ptr_to_arr)[10]; // Pointer to an array of 10 integers
ptr_to_arr = &arr; // Assigning the address of 'arr' to 'ptr'
// Accessing and display the elements of the array using the pointer
for (int i = 0; i < 10; i++)
{
printf("Element %d: %d\n", i, (*ptr_to_arr)[i]);
}
return 0;
}
In the program given above, we have declare an array `arr` of size 10 and initialized it with some values. Then, we declared a pointer ` ptr_to_arr ` to an array of 10 integers. We have assigned the address of `arr` to ` ptr_to_arr ` using the `&` operator.
Next, we used a `for` loop to access and print the elements of the array using the pointer. The `(* ptr_to_arr)[i]` syntax have been used to dereference the pointer and access the elements of the array.
When you run this program, it will output the elements of the array:
Element 0: 11
Element 1: 21
Element 2: 13
Element 3: 14
Element 4: 51
Element 5: 20
Element 6: 40
Element 7: 50
Element 8: 90
Element 9: 70
This program demonstrate how do we use a pointers to an array in C programming to an array to indirectly manipulate and access the elements of the array.
Previous Topic:-->> Use of Pointers in C. || Next topic:-->>Pointer to Function in C.
Other Topics:
Variables and Identifiers
Relational Operators
if-else statements
Switch case
While Loop
Infinite while Loops
C FOR Loop
Infinite for Loops
Continue in Loops
One Dimensional Array
Two Dimensional Arrays
Read and Display 2D Arrays
Types of functions
Passing Array To Functions
Nesting of Function
Array vs Structure
Array of Structure
Structures and Functions
Structures Within Structures
Use Of Pointers In C
File Handling In C
Loops FAQ
Arrays FAQ
count vowels in a file
Function FAQ
Conditional Statements Assignments
For Loops Assignments
Arrays Assignments
Function Assignments
Structure Assignments
Pointers Assignments
Files Assignments
Storage classes Assignments
Binary Files
count words,lines in a file
Copy files
Update File
Continue in Loops
break in Loops
Difference Between While and Do while
difference while do..while & for
malloc
calloc
Storage Classes
Operators MCQ
Conditional Statements MCQ
Loops MCQ
Arrays MCQ
Function MCQ
Structure MCQ
Pointers MCQ
Files MCQ
Storage classes MCQ