Pointer to function
As we have learned in previous tutorial that we can create a pointer of any data type such as int, char, float etc. In c program a pointer pointing to function can also be created.
The function code resides in memory and occupies some space. which means the function has some unique address. We can find the address of memory by use of function pointer.
"Function pointer in C language is defined as a variable which hold the address of a function."
Function pointer Declaration
we have learned that the functions have some specifice addresses.
So with the help of these information we can create a pointer that can contain thsese address and can point to the function.
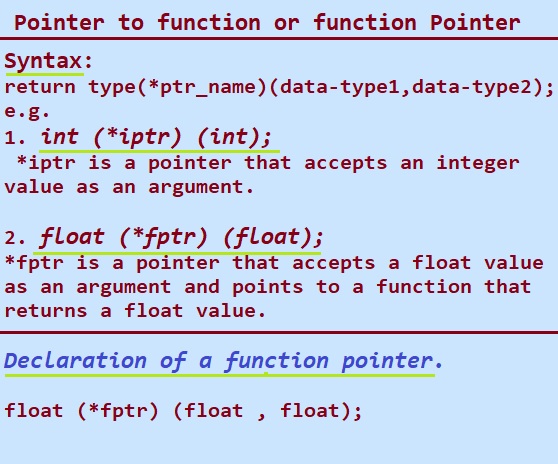
Syntax of function pointer:
return type (*ptr_name)(data-type1, data-type2…);
For example:
1. int (*iptr) (int);
Here in this example,
*iptr is a pointer that accepts an integer value as an argument
And points to a function which returns an int value.
2. float (*fptr) (float);
In the above declaration, *fptr is a pointer that accepts a float value as an argument and points to a function that returns a float value.
From given above example we can conclude that the declaration of a function pointer is same as to the declaration of a function except the pointer is preceded by a ‘*’ dereference operator. fptr is a declared as function.
Example to find the address of a function.
The Program given prints the address of main() function.
#include <stdio.h>
int main()
{
printf("Address of main() function is %p",main);
return 0;
}
Output
The address of main() function is 0x600638
From the given output we can conclude that the main() function has occupied some memory space and has some unique address.
From the above program we can say that In c programming every function has some unique address.
Assign the address of a function to the function pointer.
1. float (*fptr) (float , float); // Declaration of a function pointer.
2. float func( float , float ); // Declaration of function.
3. fptr = func; // Assigning address of func to the fptr pointer.
In the above declaration, 'fptr' pointer contains the address of the 'func' function.
function need to have declared before assigning its address to function pointer
Calling a function through a function pointer
We already know how to call a function in the usual way. Now, we will see how to call a function using a function pointer.
Suppose we declare a function as given below:
float func(float , float); // function declaration.
The given function above is called using the the way given below::
result = func(a , b); // Calling a function using usual ways.
Calling a function using a function pointer:
result = (*fptr)( a , b); // Calling a function using function pointer.
Or another way to call function.
result = fptr(a , b); // Calling a function using function pointer
The effect of calling a function by its function pointer or name is the same.
when a function pointer is used the indirection operator can be omited .
but we can still use the indirection operator as it makes clear to programmer that we are using function pointer.
C program to understand the function pointer, to add two floating point values
#include <stdio.h>
float addition(float,float);
int main()
{
float x,y;
int (*fptr)(float,float);
float res;
printf("Enter the values of x and y : ");
scanf("%f %f",&x,&y);
fptr=addition;
res=(*fptr)(x,y);
printf("Addition of %.2f + %.2f=: %.2f",x,y,res);
return 0;
}
float addition(float x,float b)
{
float c=x+y;
return c;
}
Output:
Enter the value of x and y
50.20
5.70
Value after addition is : 55.90
Passing a function's address as an argument
Function's address can be pass to other function as arguments. This way of passing argument is same as we send arguments to other function.
Let's understand through an example.
#include <stdio.h>
void hi(void (*funptr)());
void hello();
int main()
{
hi(hello);
return 0;
}
void hi(void (*funptr)())
{
printf("Function hi is called");
(*funptr)();
}
void hello()
{
printf("\nFunction hello is called");
}
Output:
Function hi is called
Function hello is called
In the above code, we have created two functions, i.e., hi() and hello(). The hi() function contains the function pointer as an argument. In the main() method, the hi() method is called in which we pass the address of hello. When hi() function is called, 'funptr' contains the address of 'hello'. Inside the hi() function, we call the hello() function by dereferencing the pointer 'funptr' as it contains the address of hello.