Output: The output in Programming defined as the information that it displays on a screen or prints on paper as a result of a particular program.
In this tutorial we will learn how output print() function is used in python .
print():The print() is the output function in python takes in any number of parameters, and prints them out on one line of text .
The print() function takes in any data as strings, and prints those values to standard out(output device). print() is a built-in function available in python library that prints the given object to the standard output console or a device.
print() function accepts several arguments,for more detail refer the diagram.
Though it is not always necessary to pass arguments in the print() function, it requires an empty parenthesis at the end that tells Python to execute the function rather than calling it by name.
output using print() in Python
Syntax : print() Function in python
Given following Syntax is print() function:
The syntax for print() function looks like this:
print(*objects,sep=' ',end='\n', file=sys.stdout,flush=False)
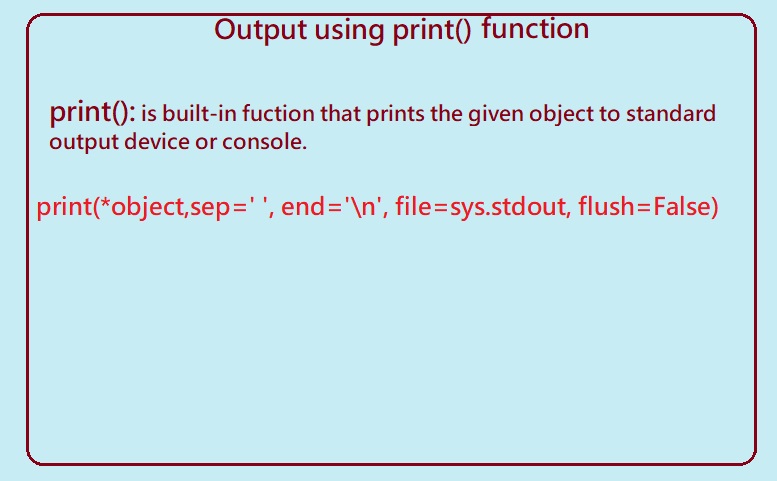
Given fig. shows the syntax and working of print() function in python.
print() function in python shows output on console.
python print() function has several arguments.
*objects: (required) – the objects that are to be printed. It can be multiple comma-separated objects or a single object.
end: The end Parameter in the print() function is used to add any string at the end of output. By default print() ends with newline '\n'
sep: objects in output are separated by sep.
flush:decides whether to flush the stream or not. If yes, the stream is forcibly flushed. Default value is False.
file: must be an object with a write(string) method; if it is not present or None, sys.stdout will be used.
Example : Python script to understand the print() function
Example 1.
print(10, 11, 12)
print(10, 11, 12, sep='*')
print(11, 12, sep='#', end='%')
Output:
10 11 12 # Here we have space between values by default.
10*11*12
11#12%
Note: All the values are followed by a comma( , ), distinguishing between themselves as separate values/objects. By default, this adds a space between the values printed as output.
Example 2:
Arithmetic operations can be directly performed inside the print function in python.
print(12 + 13) # addition
print(15 * 14) # multiplication
print(19 % 12) # modulo(remainder)
Output:
15
210
7
Example 3: We can print a string and number together.
salary = 35000
print("Your Salary " + str(salary) + " Rs only.")
Output:
Your Salary is 35000 only.
Python print() Function to Output Formatting:
Sometimes a programmer want to make the output of a code prettier and more attractive to the end user and in human redable format.
There are several ways to format output in Python.
1. Using String Modulo Operator(%)
2. Using Format Method
3. Using The String Method
4. Python’s Format Conversion Rule
1. Using String Modulo Operator(%) :
The string modulo operator ( % ) available in Python and is widely used for formating output.
# Python program showing how to use string modulo operator(%)
print("Empno : %2d, Avg Rating : %5.2f" % (1, 06.433))
print("Total Employees : %3d, Managers : %2d" % (2400, 100)) # print integer value
print("%7.3o" % (25)) # print octal value
print("%10.3E" % (356.08977)) # print exponential value
Output
Empno : 1, Avg Rating : 6.43
Total employees : 2400, Managers : 100
031
3.561E+02
2. Using Format Method
The format() method in Python formats the specified output values and insert them inside the placeholder.
The placeholder is represented using {} brackets.
The format() method after successful execution return the formatted string.
Python Programmer use {} to mark where a variable will be substituted and can provide detailed formatting.
Example 1: The Python script explain various Python string formatting techniques.
print('I love {} for "{}!"'.format('Python', 'Programming'))
# using format() method and referring a position of the object
print('{0} and {1}'.format('Python', 'Programming'))
print('{1} and {0}'.format('Python', 'Programming'))
print(f"I love {'Python'} for \"{'Programming'}!\"")
Output:
I love Python for "Programming!"
Python and Programming
Programming and Python
I love Python for "Programming!"
e.g 2 Here we take two variables and do certain operations with it.
x = 30
y = 21
mul = x * y
print('The value of x is {} and y is {}'.format(x, y))
# specifying the order of the variables.
print('{2} is the multiplication of {0} and {1}'.format(x, y, mul))
# even We can use keyword arguments to format strings.
print('Hey! Welcome to {code}. In this article we will learn about {language}'.format(code='Coding', language='Python'))
Output:
The value of x is 30 and y is 21
630 is the multiplication of 30 and 21
Hey! Welcome to coding. In this article we will learn about Python
Previous Topic:-->> Accept input in Python || Next topic:-->>Decision Making in Python