if else statement in Python are used to perform conditional operations.
if else has two part i.e. if and else.
in previous tutorial we have learned if statement to test a particular condition is true or false.
if else checks whether a given condition is true. if given condition is true the if block statements executes otherwise else block statements executes.
in Python The if else statement adds additional step in decisionn making process as compared to the basic if statement.
The starting of if else statement are similar to basic if statement.
if else Statement in Python
Syntax : if else statement in python
if (condition):
#execute this block
# if condition is true
else:
#execute this block
# if condition is false
The condition given in the above sysntax, Python always evaluates to either true or false. When if(condition): is true the code i.e.
#execute this block
# if condition is true
executes.
if condition is not true then code inside else block executes.
i.e.
#execute this block
# if condition is false
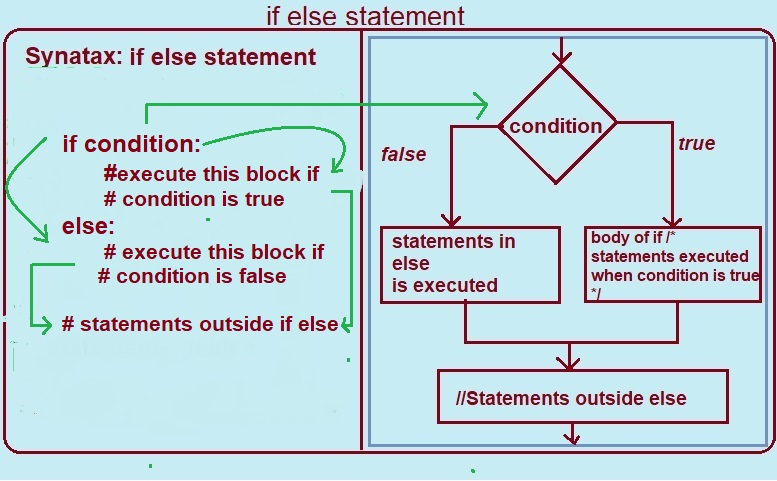
Given fig. is for the syntax and flowchart of the if else statement in python.
lets learn how syntax (if else statement) works from given Diagram.
Python starts script execution from top and goes to end.
After step by step successful execution of script the control
falls into the if statement.
after that
The flow jumps to Condition.
and begins testing the Condition
1. if the condition tested is true. then
executes statements inside if body.
i.e. ''' #execute this block
# if condition is true'''
2. if the condition tested is false. then the code inside else executes i.e.
#execute this block
# if condition is false"
"statements outside if else " always executes if the condition is true or false.
Example 1: Python script to show the use of if else statement .
p=8;
q=6;
if p<q: #test-condition
print(p," is smaller than ",q);
else:
print(q," is smaller than ",p)
Output:
6 is smaller than 8
The above program illustrates the use of if else statements to check minimum of two numbers.
1. In the above script, we have initialized two variables p, q with value as 8, 6 respectively.
2. Then, we have used if p<q: with a test-expression to check which number is the smallest . We have used a relational operator < in if statement. Since the value of p is greater than q, the condition becomes false and dose execute execute code inside body of if statement.
3. Then, control transfers to the else block and executes the code or statements i.e. print(q," is smaller than ",p) whic gives output-->6 is smaller than 8
After that, the control goes outside of the block and script terminates with a successful result.
Example 1: Python script to find Given number is Even or odd.
""" Python script to find given number is even or odd using modulus (%) Operator """
x=int(input("Enter Any Number"))
if x%2==0:
print(x," is Even")
else:
print(x," is Odd")
Output:
Enter Any Number
5
5 is Odd
Program Explanation:
x=int(input("Enter Any Number"))=: The input function Shows message "Enter Any number" on the Console. It accepts any input as String even though we enter integer values , so we have converted this input into integer using int().
if x%2==0: this expression evaluate to false. The result of x%2 is 1. Then our expression became 1==0 which is false and skip the if block, And after that control transfer to the else block and executes print(n," is Odd") statement which displays output 5 is odd.
Previous Topic:-->> if statement in Python || Next topic:-->>if else ladder in Python.