Python Language support the following assignment operators:
1. Assignment opeartor (e.g =)
2. Compound Assignment Opearators(e.g += , -=, /= ,%=,*= ,etc.)
1. Assignment Operator(=):
There is only one simple assignment operator in Python programming Language i.e. =
It is the opearator in Python Scripting (programmimg) used to assign right hand side operand to left side operand . i.e. It assign right hand side variable or value to the left hand side variable.Assignment operator which is used to assign one or more values (either string, integer, or an list, tupple or any python object) to the variable.
The General Syntax for assignment operator is
Left Operand=Right Operand
Example for Python Assignment Operator:
a = 100;
y = x; // y will becomes x
print("x = " , x); // x = ?
print("y = " , y); // y = ?
Output
x = 100
y = 100
2. Compound Assignment or Short hand Operator
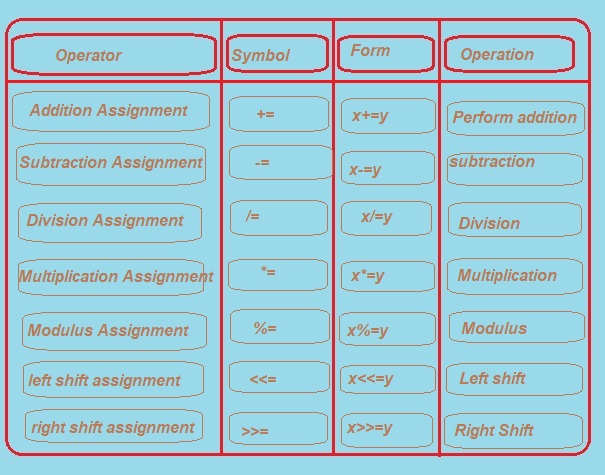
1.Addition Assignment Operator +=
+= Operator is used to perform addition of two variable or operands.
the left operand becomes equal to the addition of the right operand and left operand.
e.g x+=y
which is equivalent to x=x+y
x = 50;
y = 10;
x += y; // similar to x = x + y
print("x = " , x); // what is x now?
Output:
x=60
Program Explanation:
In the given Program the variables x and y are declared as integer and assigned values to them i.e x=50 and y=10.
x+=y which is similar to x=x+y this means in our program the instruction add the value of x=50 , y=10 and assign the addition to x itself hence value of x become 60.
2.Subtraction Assignment Operator -=
-= Operator is used to perform subtraction of two variable or operands.
the left operand becomes equal to the subtraction of the right operand and left operand.
e.g p-=q
which is equivalent to p=p-q
Example of -= operator
# C program to demonstrate -= operator #
p = 10;
q = 3;
p -= q; // similar to p = p-q
printf("p =" , p); # p=?
Output:
p=7
Program Explanation:
In the given Program the variables p and q are declared as integer and assigned values to them i.e p=10 and y=3.
p-=q which is similar to p=p-q this means in our program the instruction subtract the value of q=3 from p=10 and assign the subtraction value to p itself hence value of p become 7.
3.Multiplication Assignment Operator *=
*= Operator is used to perform Multiplication of two variable or operands.
the left operand or variable becomes equal to the multiplication of the right operand and left operand.
e.g a*=b
which is equivalent to a=a*b
here the value of a is multiplied with the value of b and the final result or calculated result is stored or assigned to a itself.
Python Script using *= Operator
/* Python program using *= Operator */
x= 10;
y = 3;
x *= y; # similar to x = x*y
print("x = " , x); # x=?
Output:
x=30
Program Explanation:
In the given Program the variables x and y are declared as integer and assigned values to them i.e x=10 and y=3.
x*=y which is similar to x=x*y this means in our program the instruction multiply the value of y=3 with the p=10 and assign the multiplication result value to x itself hence value of x become 30.
4.Division Assignment Operator /=
/= Operator is used to perform Division of two variable or operands. The division Assignment operator is an assignment operator, which divides the value of the variable by a given numeric value, which is specified on the right side of the operator.
This operator combines the two operations. First, it divides the values, and then it assigns to the variable.the left operand or variable becomes equal to the division of the right operand and left operand.
Here is some example how to use the division assignment operator in Python Programing.
e.g a/=b
which is equivalent to a=a/b
here the value of a divides with the value of b and the final result or calculated result is stored or assigned to the variable aitself.
Python script using /= Operator
/* Python script using /= Operator */
a= 8;
b = 2;
a/= b; // similar to a = a/b
print("a = " , a); # a=?
Output:
a=4
Program Explanation:
In the given Script the variables a and b are assigned values to them i.e a=8 and b=2.
a/=b which is similar to a=a/b this means in our program the instruction divides the value of a=8 by the b=2 and assign the result value to a itself hence value of a becomes 4.
5.Modulus or Modulo Assignment Operator %= The modulus Assignment operator is an assignment operator which is used to calculate the remainder of the division operation. This operator divides the value of a variable by the specified value given on the right side of the operator. After, it assigns the remainder to the variable.
Here is some example how to use the Modulus assignment operator in Python Programing.
e.g a%=b
which is equivalent to a=a%b
here the value of a divides with the value of b and the final result or calculated result i.e remainder is stored or assigned to the variable a itself.
Python Script using %= Operator
/* Python program using %= Operator */
a= 7;
b = 2;
a%= b; # similar to a = a%b
print("a = " , a); # a=?
Output:
a=1
Program Explanation:
In the given Program the variables a and b are assigned values to them i.e a=7 and b=2.
a%=b which is similar to a=a%b this means in our program the instruction divides the value of a=7 by the b=2 and assign the result value i.e remainder to a itself hence value of a becomes 1.
6.Left Shift Assignment Operator <<=
The Left shift Assignment operator is an assignment operator in Python which is used to shift or moves all the bit in first variable to the left by the number of places specified in the second variable.
Here is some example how to use the Left shift assignment operator in Python Programing.
e.g a<<=b
which is equivalent to a=a<<b
here the bits in variable a moves to the left by the number of places specified by the value of variable b
Python proram using left shift <<= Operator
/* Python program using left shift <<= Operator */
a= 7; # in binary 7 =0111
b = 1;
a<<= b; # similar to a = a<<b
print("a = " , a); # a=?
Output:
a=14
Program Explanation:
In the given Program the variables a and b are assigned values to them i.e a=7 and b=1.
a<<=b which is similar to a=a<<b this means in our program the instruction shift the value of a=7 by the b=1 to left and assign the result value i.e a=14.
Here value of a has shift to the left by b places(i.e value in b). .
In Binary number 7 is represented as =0111
when we shift these bits by 1 position to the left it becomes 1110 which is equivalent is 14 in decimal number system.
7.Right Shift Assignment Operator >>=
The Right shift Assignment operator is an assignment operator in Python which is used to shift or moves all the bit in first variable to the right by the number of places(value) specified in the second variable.
Here is some example how to use the Right shift assignment operator in Python Programing.
e.g a>>=b
which is equivalent to a=a>>b
here the bits in variable a moves to the right by the number of places specified by the value of variable b
Python proram using left shift >>= Operator
/* Python program using left shift >>= Operator */
a= 7; # in binary 7 =0111
b = 1;
a>>= b; # similar to a = a>>b
print("a = " , a); #a=?
}
Output:
a=3
Program Explanation:
In the given Program the variables a and b are assigned values to them i.e a=7 and b=1.
a>>=b which is similar to a=a>>b this means in our program the instruction shift the value of a=7 by the b=1 to the right and assign the result value i.e a=3.
Here value of a has shift to the right by b places(i.e value in b).
In Binary number 7 is represented as =0111
when we shift these bits by 1 position to the right it becomes 0011 which is equivalent is 3 in decimal number system.