 The objective of this tutorial is to learn about the Python keywords, identifiers and variables. In this topic, we are going to know about keywords in Python and how to identify them.
The objective of this tutorial is to learn about the Python keywords, identifiers and variables. In this topic, we are going to know about keywords in Python and how to identify them.
After that we will discuss different types of keywords available in Python and finally We will also brief look at Identifiers and variables with some examples.
1. Python Keywords:
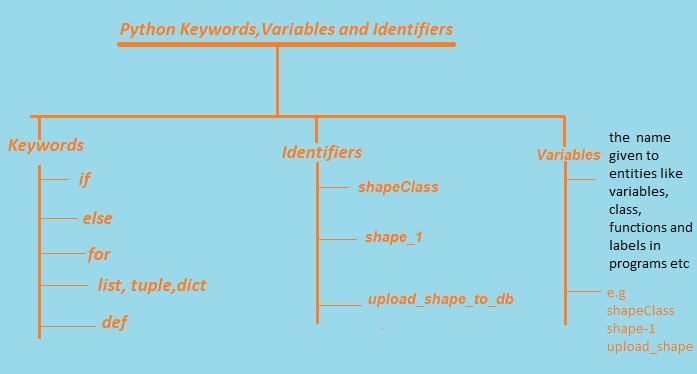
“ Keywords in Python are unique reserved words that cannot use as a variable name, function name, or other identifiers.”.
Keywords in python are used to perform some specific action or task .
Each keyword serves different purpose and all together they built python script or program or we can say vocabulary of the Python Language.
According to version 3.8 to 3.11.2 in python, there are 35 keywords that it supports. These are the basic building blocks of Python programming. Hence, you must know everything about them.
Most of them have a purpose very similar to their actual meaning in English Language.
All keywords in Python are case sensitive. So, you must be careful while using them in your code.
Example To list out or find total number of the possible Python keywords.
Python Keywords, Identifiers and Variables
# e.g Python script To list out total number of Keywords
>>>Import keyword
>>>print(keyword.kwlist)
['False', 'None', 'True', 'and', 'as', 'assert', 'async', 'await', 'break', 'class', 'continue', 'def', 'del', 'elif', 'else', 'except', 'finally', 'for', 'from', 'global', 'if', 'import', 'in', 'is', 'lambda', 'nonlocal', 'not', 'or', 'pass', 'raise', 'return', 'try', 'while', 'with', 'yield']
Another way to list out total number of Keywords in python is given below.
Just use the help() function.
e.g
>>>help(“keywords”)
or
>>>help()
after this help prompt will be displayed
help>
Here is a list of the Python keywords.
Enter any keyword to get more help.
Help>keywords
False class from or
None continue global pass
True def if raise
and del import return
as elif in try
assert else is while
async except lambda with
await finally nonlocal yield
break for not
One important thing is that we should keep in mind that the list of python keywords may change because new keywords may bring in the language and old one will not be continued in the future releases.
2.Python Identifiers:
“Identifiers” or “symbols” are the name given to entities like variables, class, functions and labels in programs etc.
If we assign some name to a programmable entity in Python, then it is nothing but technically called an identifier. Identifier must be different from any keywords. Keywords can’t be used as identifiers.
Python language lays down a set of rules for programmers to create meaningful identifiers.
Rules for naming Identifiers in Python.
1. To form meaningful an identifier use Combination of alphabets in lowercase (a to z) or uppercase (A to Z) or digits (0 to 9) or an underscore _
For example – Names like shapeClass, shape_1, and upload_shape_to_db are all valid identifiers.
>>>shapeClass=1
Is valid and following is invalid.
>>>shape Class=1
SyntaxError: invalid syntax
2. Digits cannot be used as the starting of an identifier.
For example – The name, 1Shape is incorrect, but shape1 is a valid identifier.
>>> 1shape=1
SyntaxError: invalid decimal literal
3. Keywords cannot be used as identifiers.
For example – False class from or
None is a invalid identifiers.
4. Special symbols !, @, #, $, % etc. cannot be used in an identifier.
E.g #age,@name
Following are some of the key facts about Python variables.
1. In Python Variables don’t require declaration. However, you must initialize them before use.
For example –
age = 20
The above expression will lead to the following actions.
• Creation of an object to represent the value 20.
• If the variable (age) doesn’t exist, then it’ll get created.
The variable ‘age’ is a reference to the value ’20’.
2. Whenever the expression changes, Python associates a new object (a chunk of memory) to the variable for referencing that value. And the old one goes to the garbage collector.
Example.
>>> age = 20
>>> id(20)
1716585200
>>> age = 11
>>> id(age)
1716585232
>>>
3. Also, for optimization, Python builds a cache and reuses some of the immutable objects, such as small integers and strings.
4. An object is just a region of memory which can hold the following.
• The actual object values.
• A type designator to reflect the object type.
• The reference counter which determines when it’s OK to reclaim the object.
5. It’s the object which has a type, not the variable. However, a variable can hold objects of different types as and when required.
Example.
>>> age = 20
>>> type(age)
<class 'int'>
>>> name = 'Python'
>>> type(name)
<class 'str' >
>>> name = {'Python', 'C', 'C++'}
>>> type(name)
<class 'set'>
3. Rules For Naming Python Variable: –
1. A Variable name must start with a letter or the underscore character.
2. Variable names are case-sensitive (e,g Name,name and NAME are different)
3. A Variable name cannot start with a number(eg. 9age,0name)
4. A variable name can only contain alpha-numeric character and and underscore (_,A-Z and 0-9)
e.g.
#legal Variable names
myname=”Python”
my_name=”Python”
_my_name=”Python”
myName=”Python”
MYNAME=”Python”
myname2=”Python”
#Illegal variable names
2myname=”Python”
my-name=”Python”
my var=”Python”
4. Difference Between Python Variables and Identifiers.
| Variables | Identifiers |
|---|---|
A variable is a unique name to a memory location |
Unique name given to entity is called Identifiers |
Variable names are called Identifiers |
Range of identifiers are higher than variables |
Variable is a name given to memory location that hold some kind of values |
An identifier is a name given to variable,constant, List, Tuple, Class etc. |