2. or (Logical OR) :
The condition becomes true if any one of them is non-zero(true or 1). Otherwise, it returns false i.e, 0 as the value. Below is the truth table for the logical OR operator.
This type of operator returns true even when both or even one of the conditions that are under consideration are satisfied. In any other case, it is bound to return false. For instance, the p || q will return true when both or one of p and q are true (non-zero). It also returns to be true when p and q are true.
Syntax: (condition_1 || condition_2)
e.g. If c = 5 and d = 2 then, expression ((c==5) || (d>5)) equals to 1.
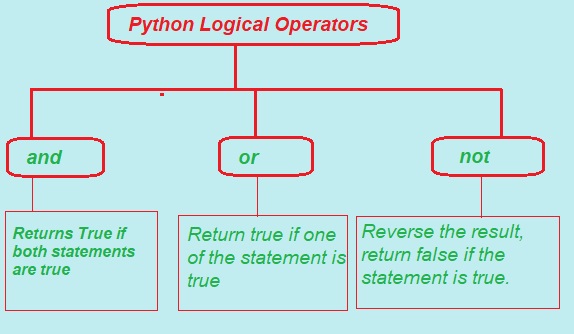
Logical Operators in Python
In this article, we are discussing the logical operators and their types. Here, we will discuss all types of logical operators used in C programming language.
As we learned in some previous article an operator can be defined as a symbol that is used for performing different operations.
C programming language has various types of operators such as arithmetic operators, relational operators, logical operators, assignment operator, increment/decrement . Let Learn Logical Operatorspers.
Logical operators in c programming are the special type of operators are generally used for combining two or more relational statements.
Upon successful evaluation any conditional statement They return Boolean values. The logical operators are used primarily in the expression evaluation to make a decision.
Logical operators in C are used to combine multiple condition. Logical Operators used in c program the expression returns either 0 or 1, it depends on the expression result true or false.
Python use following types of Logical operators:
1. and Logical AND Operator.
2. or Logical OR Operator.
3. not Logical NOT Operator.
4. ^ Logical XOR Operator.
Let us learn The Logical Operators:
The Logical Operators are special Type of word or symbol used in C Programming to connect two or more expression such that the value of expression produced depends only on that of original expression.
The Result of the Logical Comparision either true(1) or false(0), can be used to make decisions Regarding Program flow.
Let discuss them one by one.
1. and (Logical AND):
The value of an AND expression is 1 only if both input values are 1. Otherwise, the value is 0. That is, the above expression equals 1 if and only if A and B are 1. The AND operator
If both operands are non-zero, then the condition becomes true. Otherwise, the result has a value of 0. The return type of the result is int. Below is the truth table for the logical AND operator.
This type of operator returns true when both the conditions that are under consideration happen to be satisfied. In any other case, it is bound to return false. For instance, the p && q will return true when both- p and q are true (non-zero).
Syntax: (condition_1 && condition_2)
e.g If c = 5 and d = 2 then, expression ((c==5) and (d>5)) equals to false.
3. not (logical NOT):
If the condition is true then the logical NOT operator will make it false and vice-versa. Below is the truth table for the logical NOT operator.
This type of operator returns true whenever the conditions that are under condition are not at all satisfied. In any other case, it is bound to return false. For instance, the !b will return true if b is false, meaning, when b = 0.
Syntax: !(condition_1 && condition_2)
e.g. If c = 5 then, expression !(c==5) equals to 0.
4. ^(Logical XOR):
If both bits are the same then it will return false otherwise true. Below is the truth table for the logical XOR operator.
Syntax:- ((condition1) ^ (condition2))
e.g. If c = 5 and d = 2 then, expression ((c==5) ^ (d<5)) equals to 0.
| p | q | p and q | p or q | not(p) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| false | false | false | false | true |
| false | true | false | true | true |
| true | false | false | true | false |
| true | true | true | true | false |
Python Script to demonstrate Working of Logical Operator.
# Python script that shows how logical operators works.
p = 5
q = 5
r = 10
res = (p == q) and (r > q)
print("(p== q) and (r > q) is =", res);
res = (p == q) and (r < q);
print("(p == q) and (r < q) is =", res);
res = (p == q) or (r < q);
print("(p == q) or (r < q) is =", res);
res = not(p == q) or (r < q);
print("not(p == q) or (r < q) is =", res);
res = not(p != q);
print("not(p != q) is =", res);
res = not(p == q);
print("not(p == q) is =", res);
return 0;
}
Output:
(p == q) and (r > q) is True
(p == q) and (r < q) is False
(p == q) or (r < q) is True
not(p == q) or (r < q) is False
not(p != q) is True
not(p == q) is False
Program Explanation:
In the above Python script, we assign p=5,q=5 and r=10 i.e integer values are assigned to the variable.
The expression (p == q) and (r > q) evaluates to True because both operands (p == q) and (r > q) are true.
similarly Python interpreter evaluates the following expression.
(p == q) and (r < q) evaluates to false because operand (r < q) is false.
(p == q) or (r < q) evaluates to True because (p == q) is true).
not(p == q) or (r < q) evaluates to false because both operand not(p != q) and (r < q) are false.
not(p != q) evaluates to True because operand not(p != q) is false. Hence, not(p != q) is True.
not(p == q) evaluates to false because (p == q) is true. Hence, not(p == q) is false.
Previous Topic:-->> Relational Operators || Next topic:-->>Bitwise perators